Last updated: January 2021
In this Lesson, you will learn how what VDO in Linux is, and how to install, configure and manage VDO.
Contents
UNDERSTANDING THE SUBJECT MATTER
What Is VDO In Linux
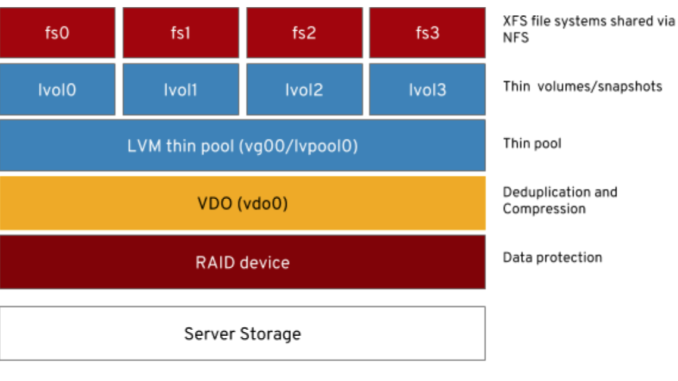
VDO (virtual data optimizer ) is a storage technology used to maximally optimize storage space by compressing and eliminating the duplication of data on a storage device.
VDO uses LZ4 for compression, increases data throughput and a VDO volume can be created from a storage device such as a block device, raid, etc.
A VDO volume is a logical volume and can be specified to be larger than the physical volume it will be created from.
If a VDO size is not specified, the VDO volume will automatically take the size of the block device which makes VDO performs better.
On the other hand, if the logical volume is larger than the block device, there will be a larger space for your data but lesser performance compared to the former. Using VDO depends on what you want to achieve in your environment.
To use VDO, the vdo service must be up and running. The kmod-vdo kernel module must also be loaded.
How To Verify If VDO Daemon Is Running
To verify if VDO is running, use the command,
[root@server1 ~]# systemctl status vdo
● vdo.service - VDO volume services
Loaded: loaded (/usr/lib/systemd/system/vdo.service; enabled; vendor preset: enabled)
Active: active (exited) since Mon 2020-11-23 17:19:19 WAT; 18min ago
How To Install VDO In Linux
To install VDO, use the command,
[root@server1 ~]# yum install vdo kmod-vdo
Updating Subscription Management repositories.
Red Hat Enterprise Linux 8 for x86_64 - BaseOS (RPMs) 0.0 B/s | 0 B 00:21
How To Start VDO In Linux
To start VDO In Linux, use the command,
[root@server1 ~]# systemctl start vdoHow To Enable VDO In Linux
To enable VDO In Linux, use the command,
[root@server1 ~]# systemctl enable vdoHow To Create a VDO Volume In Linux
To create a VDO volume in Linux without specifying the logical volume size, use the command,
# vdo create --name=<vdo-name> --device=/dev/<block-device>To create a VDO volume by specifying the logical volume size, use the command,
# vdo create --name=<vdo-name> --device=/dev/<block-dev> --vdoLogicalSize=400G
How To Start a VDO Volume In Linux
# vdo start --name=<vdo-name># vdo start --allHow To Stop a VDO Volume In Linux
# vdo stop --name=<vdo-name># vdo stop --allHow To Monitor / View The Statistics Of a VDO Volume In Linux
To view the status of a VDO volume in Linux, use the command,
# vdo status --name=<vdo-name>To view the statistics of a VDO volume in Linux, use the command,
# vdostats <vdo-name># vdostats --hu <vdo-name># vdostats --verbose <vdo-name>.
How To Delete a VDO Volume In Linux
To delete or remove a VDO volume in Linux, take the following steps below:
a). unmount the VDO volume
# umount <vdo-volume>b). delete the VDO volume.
vdo remove --name=<vdo-name>ACTION TIME
Having understood the VDO concept, let’s create a VDO volume using an example.
Step By Step Process Of How To Create a VDO Volume In Linux
create a VDO volume with a logical size of 100G and with the name, (tekneed_vdo) from (/dev/sdc). The volume should be formatted with the xfs filesystem and mounted on (vdo_data) which must be persistent across reboot.
1. verify if VDO and the kmod-kvdo module are installed. if not, install them.
[root@server1 ~]# rpm -q vdo kmod-kvdo
vdo-6.2.1.134-11.el8.x86_64
kmod-kvdo-6.2.3.114-74.el8.x86_64
On my server, they are installed but if they aren’t on your server, install them by using the command,
[root@DRDEV1 ~]# yum install vdo kmod-kvdo
Updating Subscription Management repositories.
Last metadata expiration check: 1:00:31 ago on Tue 17 Nov 2020 08:23:29 AM GMT.
Package kmod-kvdo-6.2.1.138-57.el8.x86_64 is already installed.
Dependencies resolved.
........
2. Verify the status of vdo service. If it is not started, start and enable VDO
[root@DRDEV1 ~]# systemctl status vdo
● vdo.service - VDO volume services
Loaded: loaded (/usr/lib/systemd/system/vdo.service; enabled; vendor preset: enabled)
Active: active (exited) since Mon 2020-11-16 15:31:39 GMT; 17h ago
VDO is started and enabled on my server. If it is not on your server, start and enable VDO by using the command,
[root@server1 ~]# systemctl enable --now vdo3. create a vdo volume.
On my system. i will be creating the VDO volume on the sdc device with the name, tekneed_vdo.
Let’s list the devices on the system.
[root@server1 ~]# lsblk
NAME MAJ:MIN RM SIZE RO TYPE MOUNTPOINT
sda 8:0 0 15G 0 disk
├─sda1 8:1 0 1G 0 part /boot
└─sda2 8:2 0 14G 0 part
├─rhel-root 253:0 0 12.5G 0 lvm /
└─rhel-swap 253:1 0 1.5G 0 lvm [SWAP]
sdb 8:16 0 2G 0 disk
sdc 8:32 0 10G 0 disk
sr0 11:0 1 7.3G 0 rom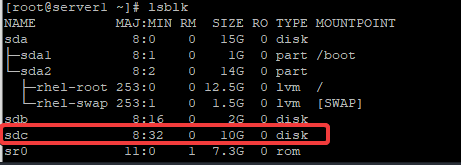
create a VDO volume with a logical size of 100G. Though the original size of the disk is 10GB. We already explained in the “UNDERSTANDING THE SUBJECT MATTER” section that you can specify a logical volume size or not.
[root@server1 ~]# vdo create --name=tekneed_vdo --device=/dev/sdc --vdoLogicalSize=100G
Creating VDO tekneed_vdo
vdo: ERROR - Kernel module kvdo not installed
vdo: ERROR - modprobe: FATAL: Module kvdo not found in directory /lib/modules/4.18.0-147.el8.x86_64
NOTE: if you get the error above, it is a common bug with VDO as of when this article is written.
There are two workarounds. Either of the two workarounds below will work.
a). Try loading the kvdo module.
[root@server1 ~]# modprobe kvdo
modprobe: FATAL: Module kvdo not found in directory /lib/modules/4.18.0-147.el8.x86_64
b). if loading the kvdo module doesn’t work, reboot your system.
[root@server1 ~]# rebootNow, Create the VDO volume
[root@server1 ~]# vdo create --name=tekneed_vdo --device=/dev/sdc --vdoLogicalSize=100G
Creating VDO tekneed_vdo
Starting VDO tekneed_vdo
Starting compression on VDO tekneed_vdo
VDO instance 0 volume is ready at /dev/mapper/tekneed_vdo
4. verify the created VDO volume
[root@server1 ~]# vdo list
tekneed_vdo5. verify the vdo status
[root@server1 ~]# vdo status --name=tekneed_vdo
VDO status:
Date: '2020-11-20 21:28:03+01:00'
Node: server1
Kernel module:
......................6. verify if compression and deduplication are enabled.
[root@server1 ~]# vdo status --name=tekneed_vdo |grep -i deduplication
Deduplication: enabled
[root@server1 ~]# vdo status --name=tekneed_vdo |grep -i compression
Compression: enabledOR
[root@server1 ~]# vdo status --name=tekneed_vdo |grep -E 'Compression|Deduplication'
Compression: enabled
Deduplication: enabled
7. Format the VDO volume with a filesystem, xfs
[root@server1 ~]# mkfs.xfs -K /dev/mapper/tekneed_vdo
meta-data=/dev/mapper/tekneed_vdo isize=512 agcount=4, agsize=6553600 blks
= sectsz=4096 attr=2, projid32bit=1
= crc=1 finobt=1,
.............8. Register the new device in the kernel.
[root@server1 ~]# udevadm settle9. Create a mount point.
[root@server1 ~]# mkdir /vdo_data10. Map the VDO device to the mount point.
[root@server1 ~]# mount /dev/mapper/tekneed_vdo /vdo_data/11. Verify if it has been mounted.
[root@server1 ~]# df -h |grep vdo_data
/dev/mapper/tekneed_vdo 100G 746M 100G 1% /vdo_data12. get the device UUID
[root@server1 ~]# lsblk --output=UUID /dev/mapper/tekneed_vdo
UUID
71c9fada-81f9-4d84-b157-7b2edbb0e191
OR
[root@server1 ~]# blkid -p /dev/mapper/tekneed_vdo
/dev/mapper/tekneed_vdo: UUID="71c9fada-81f9-4d84-b157-7b2edbb0e191" TYPE="xfs" USAGE="filesystem"13. input the device UUID in the fstab file.
[root@server1 ~]# vim /etc/fstabUUID=71c9fada-81f9-4d84-b157-7b2edbb0e191 /vdo_data xfs defaults,x-systemd.requires=vdo.service 0 0
14. do a “mount -a” to ensure that the filesystem is properly mounted.
[root@server1 ~]# mount -a15. If you wish, you can restart your system.
Let’s do a test
I mentioned that VDO manages files or data that are the same by compression and deduplication.
In this test, we will copy files of the same data multiple times to tekneed_vdo volume. We will verify the initial saving percentage before copying and the saving percentage after copying.
Let’s begin.
1. Verify the initial space of the filesystem
[root@server1 ~]# vdostats --hu
Device Size Used Available Use% Space saving%
/dev/mapper/tekneed_vdo 10.0G 4.0G 6.0G 40% 99%

You can see that the volume size is 10G, used space is 4G which VDO has already taken, available space is 6G, and “space saving” is 99%
2. copy file1 to the VDO device
[root@server1 ~]# cp -r file1 /vdo_data/file1Verify the statistics again
[root@server1 ~]# vdostats --hu
Device Size Used Available Use% Space saving%
/dev/mapper/tekneed_vdo 10.0G 4.2G 5.8G 41% 28%
You can see that the new savings is 28%
3. copy file1 to the VDO device again
[root@server1 ~]# cp -r file1 /vdo_data/file2verify the statistics
[root@server1 ~]# vdostats --hu
Device Size Used Available Use% Space saving%
/dev/mapper/tekneed_vdo 10.0G 4.2G 5.8G 41% 58%
You can see that the new savings has increased to 58% instead of decreasing further from 28%.
4. copy file1 to the VDO device again
[root@server1 ~]# cp -r file1 /vdo_data/file3Verify again.
[root@server1 ~]# vdostats --hu
Device Size Used Available Use% Space saving%
/dev/mapper/tekneed_vdo 10.0G 4.2G 5.8G 41% 78%
Did you notice that the used space has remained the same while the savings space kept increasing?
This simple test has ascertained the fact that VDO is one of the finest storage technology in Linux for space efficiency.
You May Also Like:
(Managing Layered Storage With Stratis In Linux)
Click to Watch The Lesson Video On Managing VDO in Linux
RHCSA 8 EX200 Exam Practice Question and Answer On VDO In Linux
Your feedback is welcomed. If you love others, you will share with others
Despite rebooting and running mod probe I still get the error message on both my VM’s Module kvdo not found in directory /lib/modules/4.18.0-240.10.1.el8_3.x86_64
what can I do please?
Rebooting (reboot) or simply loading the module (modprobe kmod-kvdo) should work. Are you sure your VM is not broken in anyway? Install vdo and kmod-kvdo again by using the command, (yum install vdo kmod-kvdo). It will upgrade it if it already installed. That should be able to fix the problem.
It still didn’t work apparently its a problem with kmod-kvdo not working with the latest CentOS 8 kernel and quite a number of people have similar issues.
http://ftp.halifax.rwth-aachen.de/puias/8.3/x86_64/os/BaseOS/Packages
/https://bugzilla.redhat.com/show_bug.cgi?id=1907968
Hi VICTOR,
I m encountering this error when I try to create VDO volume.
[benjm@newrhel8server ~]$ lsblk
NAME MAJ:MIN RM SIZE RO TYPE MOUNTPOINT
sda 8:0 0 20G 0 disk
├─sda1 8:1 0 1G 0 part /boot
└─sda2 8:2 0 19G 0 part
├─cl-root 253:0 0 17G 0 lvm /
└─cl-swap 253:1 0 2G 0 lvm [SWAP]
sdb 8:16 0 20G 0 disk
└─sdb1 8:17 0 10G 0 part
sr0 11:0 1 7.7G 0 rom /run/media/user1/CentOS-8-2-2004-x86_64-dvd
[benjm@newrhel8server ~]$ sudo vdo create –verbose –name=myvdo1 –device=/dev/sdb –vdoLogicalSize=200G
Creating VDO myvdo1
grep MemAvailable /proc/meminfo
vdo: ERROR – Not enough available memory in system for index requirement of 256M
the vdo status is active and kmod-kvod module is installed. What may be the issue?
Hi Ben,
your sdb device has a partition already. You need to partition sdb to sdb2, at least 10G. You can then create a VDO volume on sdb2
I have same error
Last login: Fri Jul 9 07:42:53 PDT 2021 on pts/0
[root@localhost ~]# lsblk
NAME MAJ:MIN RM SIZE RO TYPE MOUNTPOINT
sda 8:0 0 10G 0 disk
├─sda1 8:1 0 300M 0 part /boot
├─sda2 8:2 0 1G 0 part [SWAP]
└─sda3 8:3 0 8.7G 0 part /
sdb 8:16 0 5G 0 disk
├─sdb1 8:17 0 1G 0 part
│ └─vg1-lv1 253:1 0 1000M 0 lvm /personal
└─sdb2 8:18 0 1G 0 part
└─vg2-lv2 253:0 0 1016M 0 lvm /personal2
sdc 8:32 0 1G 0 disk
sr0 11:0 1 1024M 0 rom
[root@localhost ~]# vdo create –name=vdo1 –device=/dev/sdc –vdoLogicalSize=2G
Creating VDO vdo1
vdo: ERROR – Not enough available memory in system for index requirement of 256M
[root@localhost ~]#
Can anyone help please
try using a volume that is 5gb and above and try again, your sdc is just 1G
I had similar issue and by extending RAM size to 2 GB its resolved the issue, basically it was due to low ram size it was not getting add vdo process into RAM.
In question 33. I think you should mount lvm disk in fstab with
defaults,x-systemd.requires=vdo.service
Same issue in my system
[root@localhost ~]# lsblk
NAME MAJ:MIN RM SIZE RO TYPE MOUNTPOINT
sda 8:0 0 10G 0 disk
├─sda1 8:1 0 1G 0 part /boot
└─sda2 8:2 0 9G 0 part
├─cl-root 253:0 0 8G 0 lvm /
└─cl-swap 253:1 0 1G 0 lvm [SWAP]
sdb 8:16 0 10G 0 disk
sr0 11:0 1 1024M 0 rom
[root@localhost ~]# vdo create –name=vdough –device=/dev/sdb –vdoLogicalSize=100G
Creating VDO vdough
vdo: ERROR – Not enough available memory in system for index requirement of 256M
[root@localhost ~]#
Greetings,I run into the same problem “Failed to start vdo.service: Unit vdo.service not found.”,when trying to start vdo service from systemctl start vdo. Please how can I solve this problem?