
Last updated: July 2020
UNDERSTANDING THE SUBJECT MATTER
Having understood all the concepts and terminologies of software installation in Linux part 1, including what yum in Linux is, it will be a good idea to start part 2 with the installation of software using the yum package manager.
ACTION TIME
The yum package manager as we mentioned in part 1 is a tool that manages a software/package in Linux. Below are the basic examples one can do with the yum package manager.
How To Use yum install / How To Install Packages/Software In Linux Command line (RHEL/centOS 7&8)
- To install a package, you use the command,
yum install <package-name>
For example, to install the package httpd, you use the command,
[root@lab02 ~]# yum install httpd- To install more than one package at the same time, for example, if you want to install the package httpd and vsftpd at the same time, you use the command,
[root@lab02 ~]# yum install httpd vsftpd- To install a package without a confirmation to type Y/D/N, you use the command,
[root@lab02 ~]# yum install httpd -yIf you are sure of the package, yum in Linux can allow you to install a package without having to always type y for confirmation all the time.
How To Use yum To Install A Package Group on RHEL/CentOS 7&8
- To install a package group, you use the command,
yum group install <package_group>
For example, to install the package group, “Smart Card Support”, you use the command,
[root@lab02 ~]# yum group install "Smart Card Support"How To Use yum To Display A Package Information On RHEL/CentOS 7&8
- To display a package information, you use the command,
yum info <package-name>
For example, to display the information of the package httpd, you use the command,
[root@lab02 ~]# yum info httpdHow To Use yum To Delete / Remove A Package On RHEL/CentOS 7&8
- To remove a package, you use the command,
yum remove <package name>
For example, to delete the package, sshd, you use the command,
[root@lab02 ~]# yum remove httpd- To remove a package without the prompt, Y/D/N for you to confirm the removal, you use the command,
[root@lab02 ~]# yum remove httpd -yHow To Use yum To Remove / Delete A Package Group On RHEL/CentOS 7&8
- To remove a package group, you use the command,
yum group remove <group-name>
For example, to remove the package group, Smart Card Support, you use the command,
[root@lab02 ~]# yum group remove "Smart Card Support"How To Use yum To Check For An Available Update On RHEL/CentOS 7&8
- To check if an update is available, you use the command,
[root@lab02 ~]# yum check-updateBear in mind that the command above will check for the updates of all the packages installed on the system with their dependencies.
- To check for an update of a partiular package and its dependencies, for example, the kernel package, you use the command,
[root@lab02 ~]# yum check-update kernel
Updating Subscription Management repositories.
Last metadata expiration check: 0:23:17 ago on Sun 19 Jan 2020 02:59:51 PM UTC.
kernel.x86_64 4.18.0-147.3.1.el8_1 rhel-8-for-x86_64-baseos-rpms
kernel.x86_64 4.18.0-147.3.1.el8_1 rhui-rhel-8-for-x86_64-baseos-rhui-rpms
[root@lab02 ~]#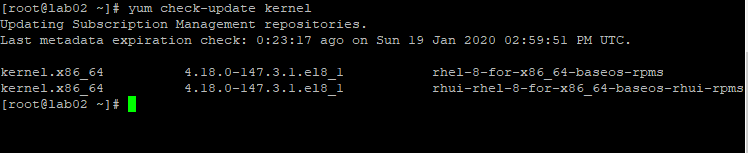
The output of the command displays the new update of the kernel package and the repositories it can found. In this case, it can be found in “rhel-8-for-x86_64-baseos-rpms” repository and “rhui-rhel-8-for-x86_64-baseos-rhui-rpms” repository.
NOTE: There are other ways to check for a kernel update without using yum in Linux

How To Use yum To Update A Software/Package On RHEL/CentOS 7&8
- To update all the software/packages on the system, you use the command,
[root@lab02 ~]# yum update- However, you may want to update just one or two software/packages. To do that, you use the command,
yum update <package>
For example, if you want to update the lvm2 package, you use the command,
[root@lab02 ~]# yum update lvm2- You may also want to update a package group. For example, if you want to update the package group “Virtualization”, you use the command,
[root@lab02 ~]# yum group update VirtualizationHow To Use yum to List A Software/Package On RHEL/centOS 7&8
- To list all packages available, both the ones installed and not installed, you use the command,
yum list --all
[root@lab02 ~]# yum list - -all- To list all the packages installed on your system, you use the command,
yum list --installed
[root@lab02 ~]# yum list - -installed- To list available packages for installation in all enabled repositories, you use the command,
yum list --available
[root@lab02 ~]# yum list --available- To list all the repositories that are enabled on your system, you use the command,
[root@lab02 ~]# yum repolist- To list all the repositories that are enabled on your system with better information compared with the command above, you use the command,
[root@lab02 ~]# yum repoinfo- To list all the repositories , both enabled and disabled on your system, you use the command,
yum repolist --all
[root@lab02 ~]# yum repolist - -allHow To Use yum To Enable and Disable A Repository On RHEL/CentOS 7&8
- To enable a repository, you use the command,
yum-config-manager - -enable <repository>
For example, to enable the repository, rhel-7-server-extras-rpms, you use the command,
[root@Linuxserver ~]# yum-config-manager - -enable rhel-7-server-extras-rpmsNOTE: subscription-manager can also be used to enable a repository without using yum in Linux
- To disable a repository, rhel-7-server-extras-rpms , you use the command,
yum-config-manager --disable <repository>
[root@Linuxserver ~]# yum-config-manager - -disable rhel-7-server-extras-rpmsNOTE: subscription-manager can also be used to disable a repository without using yum in Linux
How To Use yum To Search For A Package On RHEL/CentOS 7&8
- To search for a package, installed or not installed, to also search for a package that you don’t really know what the package name is but have an idea, you use the command,
yum search <package>
For example, to search for the package httpd, you use the command,
[root@lab02 ~]# yum search httpd
How To Use yum To List Package Groups On RHEL/CentOS 7&8
- To list the summary of the package group information on the system, you use the command,
[root@lab02 ~]# yum groups summary
Updating Subscription Management repositories.
Last metadata expiration check: 1:36:04 ago on Sun 19 Jan 2020 06:01:12 PM UTC.
Available Groups: 12
[root@lab02 ~]#
[root@Linuxserver ~]# yum groups summary
Loaded plugins: langpacks, product-id, search-disabled-repos, subscription-
: manager
There is no installed groups file.
Maybe run: yum groups mark convert (see man yum)
Available Environment Groups: 6
Available Groups: 16
Done
[root@Linuxserver ~]#
- To list all the package groups on the system, you use the command,
[root@lab02 ~]# yum group list
Updating Subscription Management repositories.
Last metadata expiration check: 1:43:20 ago on Sun 19 Jan 2020 06:01:12 PM UTC.
Available Environment Groups:
Server with GUI
Server
Minimal Install
Workstation
Virtualization Host
Custom Operating System
Available Groups:
RPM Development Tools
Container Management
.NET Core Development
System Tools
Network Servers
Development Tools
Legacy UNIX Compatibility
Security Tools
Graphical Administration Tools
Smart Card Support
Scientific Support
Headless Management
[root@lab02 ~]#
How To Use yum To Manage Recent yum Transactions On RHEL/CentOS 7&8
- To list the 20 most recent yum transaction, you use the command,
[root@lab02 ~]# yum history
- To get a detailed information about the last yum transaction done on the system, use the command,
[root@lab02 ~]# yum history info
To be specific in getting the detailed information about a particular transaction, you can use the transaction ID this way,
yum history info <id>
- To undo a recent yum transaction, use the command,
[root@lab02 ~]# yum history undo
If you know the transaction ID, you can use the command this way,
yum history undo <ID>
- To redo a recent transaction, you use the command,
[root@lab02 ~]# yum history undo
If you know the transaction ID, you can use the command this way,
yum history redo <ID>
How To Use yum To Install A Package straightaway From A Disabled Repository
To install a package from a disabled repository, the idea is that you will have to enable it and at the same time install the package. It is simultaneous.
- For example, if you want to install the package, “preupg” from a disabled repository, “rhel7-server-extras-rpms”, you use the command,
yum --enablerepo=<repo> install <package>
[root@Linuxserver ~]# yum --enablerepo=rhel-7-server-extras-rpms install preupgHow To Clean The yum Cache Using The yum Command On RHEL/CentOS 7&8
- To clean the yum cache, use the command,
[root@lab02 ~]# yum clean all
In RHEL/CentOS 7, by default, the cache files is stored in “/var/cache/yum” while in RHEL/CentOS 8, the cache file is stored in “/var/cahe/dnf“
How To Use The yum Shell To Execute multiple yum Commands On RHEL/CentOS 7&8
- yum in Linux also allows you to use a shell to write multiple commands. To use the the yum shell, you use the command,
[root@lab02 ~]# yum shell
Updating Subscription Management repositories.
Red Hat Enterprise Linux 8 for x86_64 – AppStream (RPMs) 2.6 MB/s | 14 MB 00:05
Red Hat Enterprise Linux 8 for x86_64 – BaseOS (RPMs) 2.8 MB/s | 13 MB 00:04
Red Hat CodeReady Linux Builder for RHEL 8 x86_64 (RPMs) fro 1.2 MB/s | 2.9 MB 00:02
Microsoft Azure RPMs for Red Hat Enterprise Linux 8 677 B/s | 1.4 kB 00:02
Red Hat Enterprise Linux 8 for x86_64 – AppStream from RHUI 5.4 MB/s | 14 MB 00:02
Red Hat Enterprise Linux 8 for x86_64 – BaseOS from RHUI (RP 5.1 MB/s | 13 MB 00:02
>
How To Use yum To get A Package Binaries
To get the binaries of a package, you use the command,
yum provides <package>
OR
yum whatprovides <package>
For example, to use yum provides on the httpd package, you will use the command,
[root@lab02 ~]# yum provides */httpd
Updating Subscription Management repositories.
Last metadata expiration check: 0:20:45 ago on Tue 21 Jan 2020 03:22:36 PM UTC.
httpd-2.4.37-10.module+el8+2764+7127e69e.x86_64 : Apache HTTP Server
Repo : rhel-8-for-x86_64-appstream-rpms
Matched from:
Provide : httpd = 2.4.37-10.module+el8+2764+7127e69e
httpd-2.4.37-11.module+el8.0.0+2969+90015743.x86_64 : Apache HTTP Server
Repo : rhel-8-for-x86_64-appstream-rpms
Matched from:
Provide : httpd = 2.4.37-11.module+el8.0.0+2969+90015743
yum search and yum provides are similar commands. yum search will display all the strings associated with a package name while yum provides will not only display the strings, but will also display the binaries associated with a package.
Your feedback is welcomed. If you love others, you will share with others
Leave a Reply