
Last updated: January 2021
This article will teach you what groups are, the group types, ways to create groups in Linux , how to add & remove users from a group and group management commands.
UNDERSTANDING THE SUBJECT MATTER
There are two types of groups In Linux, they are the primary group and secondary group
When a user is created, a primary group for that user is also automatically created which is the same name used in creating the user. There is no such thing as using a “group” command to create a primary group.
Creating a user is automatically creating a primary group for the user. So a user is automatically a member of its primary group.
For example, if I create a user Victor, Victor group is automatically a primary group for the user Victor. The system is designed this way for security purposes.
To buttress this, if you create a new user and open the “/etc/passwd” file where the attributes of users are found, you will notice in one of the fields, a primary group ID is automatically and just by default assigned to the user.
Similarly, open the “/etc/group” file where the group information is stored, you will by default see the name of the user as the group name with the corresponding group ID in the file.
No user can have more than one primary group but a user can be added to more than one secondary group.
The secondary group is the second, third, n.. group that a user is added to. In other words, the secondary group is the other group a user is added to. A secondary group is usually created by the administrator.
Group information is found in “/etc/group” file,
# cat/etc/group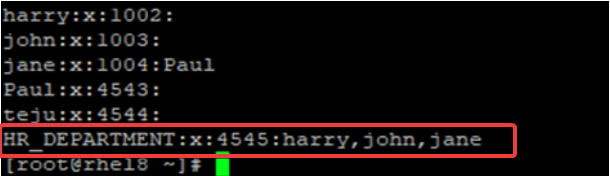
You can see the last group name at the end of the file, HR_DEPARTMENT. This group is a group created by the administrator and it has four fields.
1. The first field is the group name HR_DEPARTMENT
2. The second field is the value x which represents the group password. The password file location is “/etc/gshadow”
3. The third field is the group ID (GID), 4545
4. The last field are the names of the users in the group. In this case, harry, john and jane are members of the HR_DEPARTMENT group.

# groupadd: used to create/add a group
# usermod: used to modify users account and add users to a group
# groupdel: used to delete a group
# userdel: used to delete a user
# passwd: used to password or change users’ password.
# groupmod: used to modify group settings
# newgrp: used to login to a new group.
Having understood the concepts and terminologies behind creating groups on Linux, let’s look at some examples in the “ACTION TIME” section
ACTION TIME
How To Create and Manage Groups In Linux With Examples
Let’s start by creating groups
1. Create a group, finance
create the group,
# groupadd finance 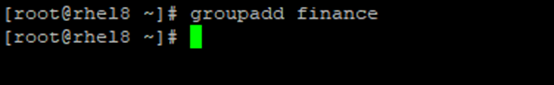
Confirm the group has been created,
# cat /etc/group 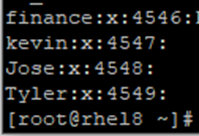
1. In the finance group, add the user kevin.
This can be done in two ways.
first method,
# usermod –aG finance kevin 
second method,
Open the /etc/group file using any text editor of your choice (vim link) and add the user kevin directly in front of the group
# vi /etc/group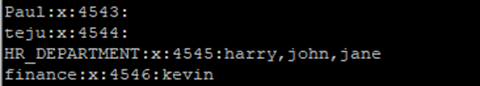
1. Create a group HR. The group ID (GID) must be 5655.
Create the group,
# groupadd –g 5655 HR 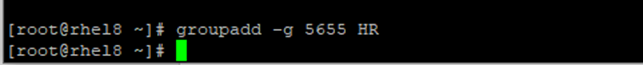
Confirm if it has been created,
# cat /etc/group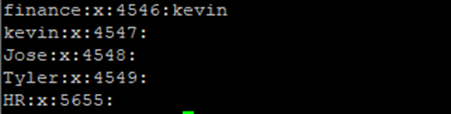
1. Remove the user kevin from the finance group
This can be done in two ways,
First method,
Open the /etc/group file and erase kevin just as it was added in example 2b.second method,
# gpasswd -d kevin finance1. Change the HR group ID (GID) to 4323
# groupmod –G 4323 HR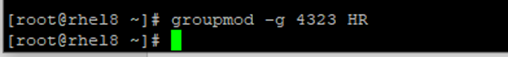
Confirm,
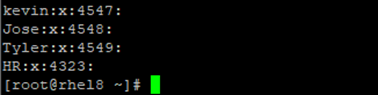
2. Which secondary group does harry belong to
# id harry
NOTE: The primary group is harry with ID 1002 while the secondary group is HR_DEPARTMENT with ID 4545
3. Change the primary group ID (harry group) of the user harry to 1322
# groupmod -g 1322 harry
NOTE: This is the same way to change a secondary group ID
Cheers!!!
Your feedback is welcomed. If you love others, you will share with others
Leave a Reply